2017 World Economic Forum Davos
ICAO Secretary General Dr Fang Liu participated in the 2017 World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davos in week ending 21 January, contributing ICAO and aviation sector perspectives to panel discussions on the Future of Travel and the Roadmap to Clean Mobility.
Dr Liu was invited to join the inaugural WEF Board of Stewards meeting on the Shaping the Future of Mobility System Initiative, the objective of which was to accelerate the transformation to a clean, safe, secure, inclusive and smart global mobility system.
EfficienSea2 booking

When mv Pearl Seaways departs Copenhagen on 31 January for her passage to Oslo, returning on 2 February, participants at the onboard conference known as e-Navigation Underway International 2017 will get a chance to learn more about EfficienSea2. Many project partners will be present at the conference to put focus on the future of e-Navigation.
This conference is co-hosted by IALA and the Danish Maritime Authority, both involved in the EfficienSea2 project, and is well-suited for highlighting latest developments in the work being carried out within EfficienSea2.
It is understood that there are some places available on this afloat conference and the organisers are doing much to ensure participants have access to the Maritime Cloud, to enable them to learn more about the first fully complete end-user service.
Integrated civil and military air navigation services

As from the beginning of the year, air traffic controllers at EUROCONTROL’s Maastricht Upper Area Control Centre (MUAC) are now providing integrated civil and military air navigation services in the Hannover Upper Information Region (UIR) – the upper airspace (above 24,500 feet) of the north-west of Germany. This was announced from EUROCONTROL’s HQ in Maastricht, The Netherlands.
Overarching objectives of the integration are to improve the air traffic management system for the benefit of both civil and military airspace users and to achieve economies of scale for all parties involved. Airspace being a finite resource, an integrated civil-military system will also generate positive effects for the European network.
Welcome RNTF and UKMPA
We extend a warm welcome to two new Corresponding Members of IAIN: RNTF and UKMPA. They joined us in the first few days of the New Year and may their time with us be fruitful.
The Resilient Navigation and Timing Foundation is based in Alexandria,
Virginia, USA, established as a non-profit, public benefit, educational and scientific charity.
RNTF has an ambitious and aggressive outreach programme to members of the
public, the navigation and timing industry, and policy makers in legislatures and administrations. Each week the organisation meets with Congressional staffs in Washington, DC, talking to staff within the executive branch of the US government, conferring with industry representatives, and corresponding with partner individuals and organisations supporting resilient navigation and timing across the globe.
The United Kingdom Maritime Pilots’ Association (UKMPA) is the representative professional body for maritime pilots in the United Kingdom. Marine pilots are highly skilled experts authorised to pilot ships in their respective districts. Taking the navigational conduct of the world’s largest vessels during the often most hazardous part of their voyage. The fundamental purpose of maritime pilotage is to ensure safety, security, environmental protection and port efficiency.
We send congratulations to Captain Donald Patrick Cockrill, Secretary-General of UKMPA who was appointed MBE in HM The Queen’s New Year Honours List for voluntary services to maritime pilotage and the port industry.
11th IHMA Congress 2018
A call for papers has been issued and the International Harbour Masters’ Association (IHMA) advises that the deadline for submission of abstracts is 19 May 2017. Submissions are invited for abstracts of 400-600 words length in respect of a proposed paper in a potential delegate’s area of expertise.
Addressing the theme Ports – essential for safe, efficient and secure global trade, the Congress programme will be designed to appeal to all responsible for the safe, secure and efficient conduct of marine operations in ports and industry organisations working with, or within, ports across all levels of the industry.
Here is an opportunity for the presentation of ideas, case studies and technical research on innovations that will promote safe, efficient and secure maritime logistics, improve cooperation between ports and ships, develop best practice, and raise global standards for the safety, security and efficiency of ports.
USS Carl Vinson CSG scheduled deployment to the Western Pacific

Nimitz-class aircraft carrier USS Carl Vinson (CVN 70), Carrier Air Wing (CVW) 2, and embarked Destroyer Squadron (CDS) 1 have been deployed with Ticonderoga-class guided-missile cruiser USS Lake Champlain (CG 57) and Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyers USS Michael Murphy (DDG 112) and USS Wayne E. Meyer (DDG 108).
While deployed, the Carl Vinson CSG will remain under US 3rd Fleet command and control, including beyond the International Date Line which previously divided operational areas of responsibility for the 3rd and the 7th Fleets. Third Fleet operating forward offers additional options to the Pacific Fleet commander by leveraging the capabilities of the 3rd and the 7th Fleets. This operational concept allows both numbered fleets to complement one another and provide the foundation of stability in the Indo-Asia-Pacific region.
A New Year message from Yasuo Arai, President of IAIN
Last year I began my message by commenting on the proliferation of autonomous marine systems. That proliferation has continued apace. To date they have been mostly small craft pre-programmed for scientific research but aspirations are growing and so is the size of vessels intended to be remotely controlled or, indeed, autonomous. IAIN is engaging in this area, most specifically by supporting the UK Marine Autonomous Systems (MAS) Regulatory Working Group to evolve a regulatory framework that will enable developers to plan their projects so as to be compliant with those regulations.
Despite activity in the US intended to encourage industry to develop a suitable non-space-based timing and positioning system to complement GNSS and the evident deliberate and significant interference to GNSS signals in some parts of the world, there does not yet seem to be a commercially viable system available for consideration. With the advent of more, and larger, MAS the necessity for a reliable timing and navigation backup to space-based positioning is evermore starkly obvious. The only system presently developed enough that it could deliver a solution to this requirement is e-LORAN. For the users, the elegant way to encompass eLORAN would be to develop a multi-system receiver capable of processing signals from some or all of the major GNSS (GPS, GALILEO, GLONASS, COMPASS) and the Regional Navigation Satellite Systems (QZSS, IRNS (or NAVIC)) and eLORAN, for they all use similar correlation techniques and they are each suitable for land, sea and air platforms.
We wish a happy, successful and safe New Year to all our Members and readers.
 Yasuo Arai,
Yasuo Arai,
(Japan Institute of Navigation)
IAIN President
Manchester and Hyderabad airports become carbon neutral

– Manchester Airport becomes the first carbon neutral airport in the UK;
– Hyderabad Airport becomes second carbon neutral airport in India and wider Asia-Pacific region;
– 37% of air passengers worldwide now travel through airports certified under the four levels of the Airport Carbon Accreditation programme.
Hot on the heels of the recent COP22 climate negotiations there have been announcement of two airports becoming carbon neutral: Manchester Airport and Hyderabad Rajiv Gandhi International Airport. Both have now achieved carbon neutral status (Level 3+), certified by the independent carbon management programme known as Airport Carbon Accreditation.
This brings the total number of carbon neutral airports around the world to 27, while the overall programme now counts 176 airports across the four available levels of certification.
The Airport Carbon Accreditation programme – launched by the airport association ACI EUROPE in 2009 – certifies airports at four different levels of accreditation covering all stages of carbon management (i) Mapping; (ii) Reduction; (iii) Optimisation and (iv) + Neutrality). It is independently administered and has the support of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP), the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), the European Union (EU) and others.
UK Parliament Transport Select Committee’s new inquiry

In the UK’s House of Commons, the Transport Committee announced it is launching a new inquiry into industry and government action in response to Maritime Growth Study, a report on the UK’s maritime sector, published by the Department for Transport in September 2015.
This report was the culmination of an in-depth study of the whole UK maritime sector: shipping and ports, and the range of associated business services. It set out a number of recommendations designed to ensure the UK maintains its status as a world-leading maritime centre, and can take advantage of opportunities for global growth.
It was therefore announced that the Transport Committee intends to monitor progress towards implementation of the study’s recommendations, and consider the adequacy of the overall strategy for the UK maritime sector, including in the context of the UK leaving the European Union.

ENC 2017 – latest news
The local organising committee of ENC2017 is progressing well with the preparation of the scientific programme for this event to be held in Lausanne from 9-12 May next. With the launch of the Galileo initial services and the evolution of the GNSS programmes the conference will have an exciting opening session and panel discussion on GNSS, it is understood.
Please note: The deadline for submitting a paper to ENC 2017 has been extended to 24 January, see the submission details for authors and the Call for Papers.
Dedicated sessions may be included in the programme, typically those associated with European Projects. Those with interests here are invited to contact Pierre-Yves Gilliéron directly at: pierre-yves.gillieron _ at _ epfl.ch.
Advice on drones – introducing the EASA
Popularly known as drones, but also referred to as remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPAS) or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) they come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from small handheld types up to large aircraft, potentially a similar size to airliners.
Just like any other aircraft, an unmanned aircraft must always be flown in a safe manner, both with respect to other aircraft in the air and also to people and properties on the ground. In the UK it is the primary aim of the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) to enable the full and safe integration of all UAS operations into the UK’s total aviation system.
Guidance for keeping drone flight safe and legal, including flying drones for fun (on non-commercial flights), is to be found here.
Introducing the EASA, the European Aviation Safety Agency
EASA’s mission is to ensure both the highest common level of safety protection for EU citizens and the highest common level of environmental protection. This is achieved with a single regulatory and certification process among Member States which, in turn, facilitates the internal aviation single market in order to create a level playing field. At the same time the Agency works with other international aviation organisations and regulators.
Tasks of EASA include the drafting of rules in all fields pertinent to the EASA mission. Furthermore, the Agency certifies and approves products and organisations in fields where EASA has exclusive competence, for example in airworthiness.
EASA’s Geo-Limitation Task Force Report can be found here.
EUROCONTROL highlights of 2016
The EUROCONTROL Network Manager covers the whole of Europe – from Ireland to Armenia and from Morocco to Finland. It handles over ten million flights a year with summer peaks of over 34,000 a day. That means an aircraft is taking off or entering European airspace every three seconds. Inevitably, there are bottlenecks. These may be in particularly busy parts of airspace or at some airports at some times of day. Any disruption, such as a runway out of action, fog, a thunderstorm or technical failure, can result in difficulties.
The Network Manager receives flight plans for all the commercial flights in its area and also receives the declared capacity limits for air traffic control centres and airports across the continent. So for example if an airport has snow or fog, it may reduce the rate at which aircraft can land. This is called a regulation. The Network Manager then looks at the whole picture and problem areas are identified – where the demand is greater than the capacity.
One solution of course is to see if the capacity can be increased. So if a controller is covering a large area and the traffic is expected to be at the limit of how many aircraft can safely be handled at a single controller position, then that area might be split into two sectors, with two controllers or teams of controllers each covering part of the traffic.
Readers are invited to take a look at a review of EUROCONTROL’s highlights of 2016.
Galileo delivers globally

Early in December the European Space Agency (ESA) announced that Europe’s own Galileo satellite navigation system had begun operating, with the satellites delivering positioning, navigation and timing information to users around the globe.
On 9 December the European Commission, owner of the system, formally announced the start of Galileo Initial Services, the first step towards full operational capability. Further launches will continue to build the satellite constellation, which will gradually improve the system performance and availability worldwide.
ICAO on UAS’s (drones)
Aimed at assisting consumers and remote pilots regardless of their skills and experience, the ICAO launched from its Montréal HQ on 13 December its new Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) Toolkit on the occasion of International Civil Aviation Day.
Commented ICAO Council President Dr Olumuyiwa Benard Aliu: ‘The resources this new toolkit makes available are designed to help UAS operators of all ages operate their aircraft safely and responsibly. The importance of recognizing that these devices are aircraft, and of integrating their use safely with existing manned operations, should not be underestimated.’
Given that UAS, informally referred to as drones, can be mistakenly and often illegally operated by less-informed pilots around airports and other areas of controlled or sensitive airspace, ICAO has been taking steps to help minimize their risks. Its new UAS Toolkit is much more than a starting point for learning
the basics of their safe operation.
Think Climate Coalition international conference
Climate change is an important and growing focus of attention. The Paris Agreement on climate change, which came into force on 4 November 2016, is an ambitious international agreement that aims to combat climate change and adapt to its effects. Coming years are likely to see massive efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and move to low carbon solutions across all sectors: navigation infrastructure is no exception. Notwithstanding the Paris Agreement, however, it is also widely agreed that continuing change in certain climate parameters is now unavoidable. Resilience will need to be strengthened and waterborne transport infrastructure will need to adapt.
The PIANC-led Think Climate Coalition announced on 20 December a major international climate change conference dedicated to the interests of waterborne transport infrastructure owners, operators and users. The event will take place at the Crowne Plaza Hotel in Brussels, Belgium on 27/28 March, 2017.
Satellite trials in Euro ATC
It was announced on 20 December that the European Space Agency (ESA) had recently completed its first flight trials using satellites to help bring Europe closer to its goal of modernising air traffic control. These trials are part of the public-private partnership between ESA and UK satellite operator INMARSAT to deliver high-capacity secure digital data links via satellite for air-ground communications for cockpit crews over European airspace under ESA’s Iris Precursor programme.
It is understood that by 2019, Iris Precursor will provide air-ground communications for initial 4D flight path control, pinpointing an aircraft in four dimensions: latitude, longitude, altitude and time. This will enable precise tracking of flights and more efficient management of traffic.
Report on the eleventh ICG meeting
The Eleventh Meeting of the International Committee on GNSS (ICG) was held in Sochi, Russian Federation from 06 to 11 November 2016.
“I took part in the last two ICG meetings and I can say that all ‘owners’ of satellite systems are having small problems with implementation of their plans for development and modernisation. Most of these problems are related to the slowdown in the development of systems and the lack of possibilities to accelerate the work. The reason for this situation is the global financial situation.”
“The most important issue is the problem of protecting GNSS from spoofing and jamming. The best solution in this field, currently, is the terrestrial alternative generally known as ‘e-Loran’ that is in development in a few countries around the world.”
Maritime Safety Committee, 97th meeting

The 97th session of the IMO Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) was held at
IMO HQ in London from 21-25 November.
Among other issues, these recommendations stand out:
– The MSC adopted recommendations on the safe carriage of more than 12 industrial personnel on board vessels engaged on international voyages, aimed at addressing the safe and efficient transfer of technicians at sea, such as those working in the growing offshore alternative energy sector.
– Also adopted were recommendations for carriage of liquefied hydrogen in bulk, as the International Gas Carrier (IGC) Code lacks specific hydrogen requirements.
– Subject to IMO Assembly confirmation, the MSC adopted amendments on a recommendation to Governments to take into account safety of navigation when multiple structures at sea, such as wind turbines, are being planned.
– Amendments were approved to update the International SafetyNET and the
NAVTEX Manuals. SafetyNET is the international automatic direct-printing satellite-based service for the promulgation of Maritime Safety Information (MSI), navigational and meteorological warnings and forecasts and other urgent safety related messages to ships, including SAR information. NAVTEX provides coastal shipping, via terrestrial means, with similar messages above by automatic display or printout from a dedicated receiver.
– The MSC approved a circular expressing grave concern over the reported
launch of missiles by the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea without due warnings.
CERGAL 2017
The major milestones on the road to the successful operational rollout of Satellite Navigation systems like GPS/EGNOS, Galileo, GLONASS and Compass (Beidou) are the qualification and certification of mission and safety critical applications.
The German Institute of Navigation DGON is offering an international symposium on certification of GNSS systems and services.
CERGAL 2017 will be held on 5-6 July 2017 at the European Space Operations Centre, Darmstadt, Germany.
For abstract submission and all details see dgon-cergal.org.
Navigation assessments – a guide to best preactice
Many maritime incidents could have been prevented by the use of a navigation assessment. The way that an assessment should be conducted to the best advantage of ship operator and crew alike is the subject of a new book published by The Nautical Institute.
Navigation Assessments: A Guide to best practice explains how an assessment conducted in a positive and constructive way can provide tangible benefits for maritime safety while contributing to the professional development of bridge team members.
The use of the term ‘assessment’ rather than ‘audit’ is intended to emphasise the positive and to encourage crews to be truthful with assessors. An assessment should be conducted over several days at sea so that the assessor can gain an understanding of the culture on board and identify the navigation team members’ strengths and weaknesses. Coaching, consultation and feedback between assessor and bridge team can break down barriers and build stronger safety cultures.
EfficienSea2 mid-term conference report
EfficienSea 2 is an three-year EU Horizon 2020 funded project led by the Danish Maritime Authority (DMA), with 32 partners. Its mid-term conference was held in Copenhagen on 8 and 9 November 2016, aiming to give both industry and other actors outside the project a chance to become familiar with and give feedback on the e-Navigation solutions being developed by EfficienSea2.
‘Safe connectivity made easy’ were the defining words of the conference. Two platforms – the Maritime Cloud and the BalticWeb – were released in BETA
versions and demonstrated with a number of services.
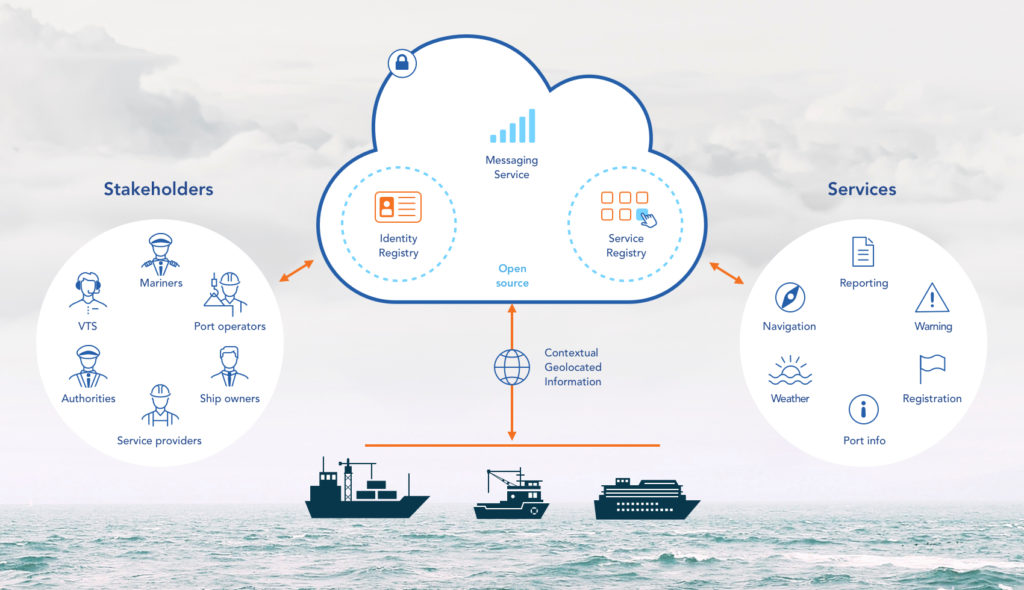
The Maritime Cloud was the first thing to be demonstrated at the conference. Consisting of a service registry, an identity registry and a management portal, the Maritime Cloud will make it possible to connect the end user of services with the service providers in a way which is both user friendly and safe.
The BalticWeb was introduced as a platform for e-navigation services. Demonstrations were given of harmonized, digital navigation services, including real-time chart updates, navigational warnings and notices to mariners. Smart wayfinding using data overlays was presented, with optimized routeing on the Baltic Web, using weather and ice prognosis as a way of finding efficient routes, as well as space weather prediction for more accurate navigation. Sea/shore integration was demonstrated, with route sharing ship-to-shore and information sharing between Vessel Traffic Services/Ship reporting Systems (VTS/SRS) for efficient SAR operations.
MLA College wins Gold Award
It was reported on 1 December that Marine Learning Alliamce College had won the Gold award for the Best Online Distance Learning Programme at the Learning Technologies Awards 2016 in London on 30 November for their submission: Delivering degrees to seafarers without internet.
The panel of independent academics judging the submission were impressed with the way MLA College combined innovative technology with traditional academic tutoring that was personalised to each student, enabling a whole new generation of seafarers to gain a higher qualification whilst remaining in their full-time job.
The Awards gathered 800 people to celebrate the best learning technologies across the world, with shortlisted entries from Canada, Australia, New Zealand, India, USA, Turkey, Germany, Hungary, Switzerland, Spain and Italy.
Maps and the 20th century: drawing the line

© British Library, photo by Clare Kendall.
A major new exhibition at the British Library, 4 November 2016 – 1 March 2017, looks at the history of the 20th century through its maps for the first time, shedding new light on familiar events, from global conflicts to the depths of the ocean floor – and even the mapping of outer space. It explores how 20th century maps shaped the ways we see the world we live in. Furthermore, it celebrates the rare beauty and astonishing variety of 20th century maps from the first sketch of the London Underground from 1931, to declassified Ministry of Defence maps, Ordnance Survey maps from the 1920s, a Russian moon globe and the first map of Winnie the Pooh’s Hundred Acre Wood.
From questions of war and peace, to understanding the movements of people, nature, and even the financial markets, Maps and the 20th Century: Drawing the Line explores how maps became increasingly present in 20th century lives.
The exhibition looks at the spectacular advances in the technology of mapping across the century, from the land surveys of 1900 to the development of satellite imagery by 2000. For the first time, we could see from the Atlantic Ocean floor to the far side of the Moon. Telling the history of the 20th century in maps allows us to reconsider the recent past from different perspectives.
Light in the darkness
Light in the darkness: a history of lightships and the people who served on them by Liam Clarke. This 160 page paperback examines the origins of the lightship services of Great Britain and Ireland, the obstacles and prejudices that faced originators of the idea and the subsequent development of the vessels and working practices over the years.
Dr Clarke has certainly been dedicated in his extensive research and uses in many places his own illustrations.
Since Hamblin’s lightship of 1731 the dangerous occupation of lightsman has claimed the lives of a number of crews and those who tried to save them in peace and in war. The lives and working conditions of the brave men who put their lives at risk guiding ships safely to their ports without peril, has been almost forgotten although some of the ships in which they fared continue to serve the mariner in an automated state monitored from shore. Indeed, some have hulls half a century old, testament surely, to sound materials and good ship husbandry.
Orders may be placed at Amberley Publishing.
IMO awards for exceptional bravery at sea
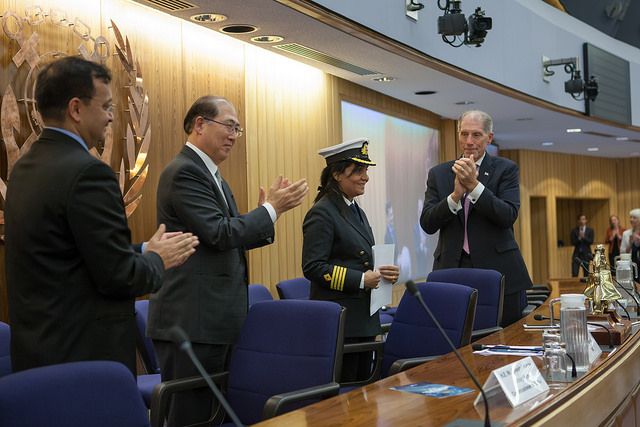

The IMO Award for Exceptional Bravery at Sea was established by IMO to provide international recognition for those who, at the risk of losing their own life, perform acts of exceptional bravery, displaying outstanding courage in attempting to save life at sea or in attempting to prevent or mitigate damage to the marine environment. For 2016, 23 nominations were received from nine Member States and one inter-governmental organization.
The Master of an Indian oil tanker who says she was “just doing her job” has received the highest IMO bravery recognition for saving the lives of seven fishermen from a sinking fishing boat during a tumultuous storm in the Bay of Bengal in June 2015.
‘It is every seafarer’s and Master’s solemn duty and obligation to save souls in distress at sea. I just did what a seafarer should do for a fellow soul in distress at sea. Yes, it was an instant decision, but not without assessing the risks involved. I just did my duty,’ said Captain Radhika Menon, Master of the oil products tanker Sampurna Swarajya.